Advanced Grammar
Youth Language Arts | Grades 7-10
Mastering the Structure of Language

Parts of speech
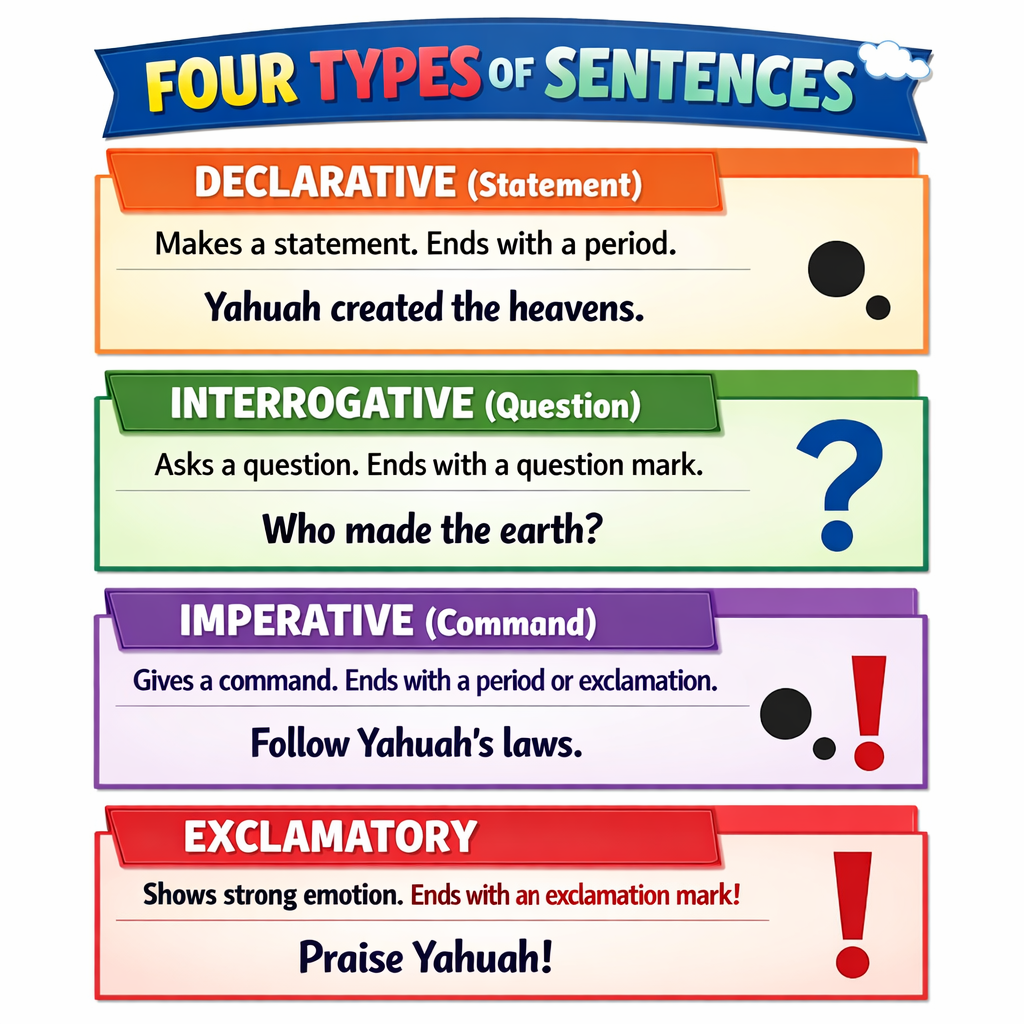
Types of sentences
Lesson 1: Sentence Structure - The Four Types
Every sentence in English falls into one of four structural categories based on how many clauses it contains and what types of clauses. A clause is a group of words containing a subject and a verb.
Independent clause: Can stand alone as a sentence (expresses a complete thought).
Dependent clause: Cannot stand alone; depends on an independent clause for meaning.
1. Simple Sentence
Contains ONE independent clause (may have compound subjects or verbs).
Simple "Yahuah is my shepherd."
Simple "David and Jonathan were close friends and loved each other deeply."
2. Compound Sentence
Contains TWO or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction (FANBOYS: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so) or a semicolon.
Compound "Moses stretched out his hand, and the sea divided."
Compound "The wicked flee; the righteous are bold as a lion."
3. Complex Sentence
Contains ONE independent clause and ONE or more dependent clauses.
Complex "When Pharaoh refused to listen, Yahuah sent the plagues."
Complex "The man who trusts in Yahuah shall be blessed."
4. Compound-Complex Sentence
Contains TWO or more independent clauses AND at least ONE dependent clause.
Compound-Complex "Although the flood covered the earth, Noah and his family were saved, and they began a new life."
Good writers use a variety of sentence structures to create rhythm, emphasis, and flow. Too many simple sentences sound choppy. Too many complex sentences can be hard to follow.
"In the beginning Elohim created the heavens and the earth. The earth was without form, and void; and darkness was on the face of the deep. And the Spirit of Elohim was hovering over the face of the waters."
— Genesis 1:1-2Identify each sentence as Simple (S), Compound (Cd), Complex (Cx), or Compound-Complex (CC):
1. "Yahuah is my light and my salvation."
2. "The fool has said in his heart that there is no Elohim."
3. "Abraham believed Yahuah, and it was credited to him as righteousness."
4. "When Daniel knew the decree was signed, he went home, and he prayed as he always did."
5. "The heavens declare the glory of El."
1. A _______________ sentence contains one independent clause.
2. A _______________ sentence contains two or more independent clauses joined by a coordinating conjunction.
3. A _______________ sentence contains one independent clause and at least one dependent clause.
4. The coordinating conjunctions can be remembered by the acronym _______________.
5. A dependent clause _______________ stand alone as a sentence.
Combine these simple sentences into the type indicated:
Compound: "The Israelites crossed the Red Sea. The Egyptian army pursued them."
Complex: "David defeated Goliath. He trusted in Yahuah."
Write one example of each sentence type about a biblical event:
Simple:
Compound:
Complex:
Compound-Complex:
Answer Key - Lesson 1
Recall: 1) S, 2) Cx, 3) Cd, 4) CC, 5) S
Recite: 1) simple 2) compound 3) complex 4) FANBOYS 5) cannot
Lesson 2: Phrases and Clauses
Phrase: A group of related words that does NOT contain both a subject and a verb.
Clause: A group of words that DOES contain both a subject and a verb.
Types of Phrases
- Prepositional: "in the beginning," "through the wilderness"
- Participial: "walking in righteousness," "having been delivered"
- Gerund: "Keeping the commandments is a blessing."
- Infinitive: "to love Yahuah," "to walk humbly"
- Appositive: "Moses, the servant of Yahuah, spoke."
Types of Dependent Clauses
- Adverb clause: tells when, where, why, how → "When he saw the city, Yahusha wept."
- Adjective clause: modifies a noun → "The man who trusts in Yahuah is blessed."
- Noun clause: functions as a noun → "What Yahuah requires is justice."
Identify each underlined part:
1. "By faith, Abraham obeyed."
2. "The prophet who spoke the truth was rejected."
3. "Walking through the valley, David feared no evil."
4. "When the trumpet sounds, the dead shall rise."
5. "We are called to be holy."
1. A _______________ is a group of words without a subject-verb pair.
2. A _______________ is a group of words with a subject-verb pair.
3. An adjective clause modifies a _______________.
4. A prepositional phrase begins with a _______________.
5. An infinitive phrase begins with "_______________" plus a verb.
Expand each sentence by adding the phrase type indicated:
"David prayed." (Add prepositional phrase)
"The disciples followed." (Add participial phrase)
Answer Key - Lesson 2
Recall: 1) Prepositional phrase 2) Adjective clause 3) Participial phrase 4) Adverb clause 5) Infinitive phrase
Recite: 1) phrase 2) clause 3) noun 4) preposition 5) to
Lesson 3: Verbals - Participles, Gerunds, Infinitives
Verbals are verb forms that function as other parts of speech.
Participles (function as ADJECTIVES)
"The risen Messiah appeared." (past participle)
"The rejoicing multitude praised Yahuah." (present participle)
Gerunds (function as NOUNS)
"Believing is essential for salvation." (subject)
"They practiced fasting." (object)
Infinitives (function as NOUNS, ADJECTIVES, or ADVERBS)
"To love Yahuah is the first commandment." (noun - subject)
"He has the power to forgive sins." (adjective)
"Yahusha came to seek the lost." (adverb)
Identify as Participle (P), Gerund (G), or Infinitive (I):
1. "To obey is better than sacrifice."
2. "The scattered disciples preached."
3. "Fasting brings spiritual focus."
4. "They were sent to proclaim the good news."
5. "The weeping women followed."
1. A _______________ is a verb form functioning as an adjective.
2. A _______________ is a verb form ending in -ing functioning as a noun.
3. An _______________ is "to" plus the base form of a verb.
4. Gerunds and present participles both end in _______________.
Write sentences using verbals:
Gerund as subject:
Participle phrase:
Infinitive as adverb:
Answer Key - Lesson 3
Recall: 1) I, 2) P, 3) G, 4) I, 5) P
Recite: 1) participle 2) gerund 3) infinitive 4) -ing
Lesson 4: Subject-Verb Agreement
Singular subjects take singular verbs; plural subjects take plural verbs. The challenge is tricky constructions.
Phrases Between Subject and Verb
The subject is never in a prepositional phrase.
"The book of Psalms contains 150 chapters."
Compound Subjects
And = plural. Or/Nor = match nearest subject.
"Peter and John were going to the temple."
"Neither the elders nor the priest was willing."
Indefinite Pronouns
Singular: each, every, everyone, anybody, no one, neither, either
Plural: both, few, many, several
1. The promises of Yahuah (is/are) trustworthy.
2. Everyone who calls on His name (is/are) saved.
3. Moses and Aaron (was/were) sent to Pharaoh.
4. Each of the tribes (has/have) its portion.
5. Neither the scribes nor the priest (was/were) able.
1. Singular subjects take _______________ verbs.
2. The subject is never in a _______________ phrase.
3. With "or" or "nor," the verb agrees with the _______________ subject.
4. "Everyone" is a _______________ indefinite pronoun.
Correct the errors:
1. "The writings of the prophets speaks of the Messiah."
2. "Each of the apostles were given authority."
Answer Key - Lesson 4
Recall: 1) are 2) is 3) were 4) has 5) was
Recite: 1) singular 2) prepositional 3) nearest 4) singular
Lesson 5: Pronoun Case and Reference
- Subjective: I, you, he, she, it, we, they, who
- Objective: me, you, him, her, it, us, them, whom
- Possessive: my, your, his, her, its, our, their, whose
Who vs. Whom
Who = subjective (substitute "he"). Whom = objective (substitute "him").
"Who shall ascend?" (he shall ascend)
"Whom shall I fear?" (I shall fear him)
Clear Reference
Every pronoun must clearly refer to a specific antecedent.
"When Moses spoke to Aaron, he was angry." (Who?)
"When Moses spoke to Aaron, Moses was angry."
1. Peter and (I/me) went fishing.
2. Yahusha called Peter and (I/me).
3. (Who/Whom) do you say that I am?
4. (Who/Whom) is able to stand?
5. This is between Yahuah and (we/us).
1. Use _______________ case pronouns for subjects.
2. Use _______________ case pronouns for objects.
3. Use "who" when you could substitute "_______________."
4. Every pronoun must clearly refer to its _______________.
Answer Key - Lesson 5
Recall: 1) I 2) me 3) Whom 4) Who 5) us
Recite: 1) subjective 2) objective 3) he/she 4) antecedent
Lesson 6: Parallel Structure
Parallel structure means using the same grammatical form for items in a series or paired ideas.
"...what does Yahuah require of you but to do justly, to love mercy, and to walk humbly with your Elohim?"
— Micah 6:8Parallelism in Lists
"The Torah teaches faithfulness, obedience, and how to love."
"The Torah teaches faithfulness, obedience, and love."
With Correlative Conjunctions
Both...and, either...or, neither...nor, not only...but also
"He was both a prophet and served as priest."
"He was both a prophet and a priest."
Correct (C) or Faulty (F)?
1. "The apostles were praying, fasting, and they were waiting."
2. "He taught them to love Yahuah, to serve others, and to walk in truth."
3. "Faith comes by hearing and to obey the Word."
1. "We are called to worship Yahuah, serving others, and be faithful."
2. "David was a shepherd, warrior, and he wrote psalms."
Answer Key - Lesson 6
Recall: 1) F 2) C 3) F
Lesson 7: Modifiers - Placement and Clarity
Modifiers must be placed carefully to avoid confusion.
Dangling Modifiers
The word being modified is missing.
"Walking through the wilderness, the manna appeared."
"Walking through the wilderness, the Israelites found manna."
Misplaced Modifiers
The modifier appears to modify the wrong word.
"Yahusha healed the man sitting by the pool with a word."
"With a word, Yahusha healed the man sitting by the pool."
Limiting Modifiers
"Only," "just," "nearly," "almost" change meaning based on placement.
"Only Yahusha healed ten lepers." (no one else did)
"Yahusha healed only ten lepers." (exactly ten)
Dangling (D), Misplaced (M), or Correct (C)?
1. "Praying in the garden, the soldiers arrived."
2. "Filled with the Spirit, the apostles preached boldly."
3. "Peter denied the Master, weeping bitterly."
1. "Covered with sores, Abraham comforted Lazarus."
2. "Having fasted for forty days, the stones could not tempt Yahusha."
Answer Key - Lesson 7
Recall: 1) D 2) C 3) M (or C depending on reading)
Lesson 8: Active vs. Passive Voice
Active: "Yahuah created the heavens." (subject performs action)
Passive: "The heavens were created by Yahuah." (subject receives action)
When to Use Active (Most of the time)
Active voice is clearer, more direct, and more engaging.
When Passive Is Appropriate
- Actor is unknown: "The temple was destroyed in 70 AD."
- Receiver is more important: "Yahusha was crucified."
Active (A) or Passive (P)?
1. "Abraham believed Yahuah."
2. "The Messiah was rejected by the leaders."
3. "The Spirit led Yahusha into the wilderness."
4. "Many signs were performed by the apostles."
1. "The Red Sea was parted by Yahuah." → Active:
2. "David slew Goliath." → Passive:
Answer Key - Lesson 8
Recall: 1) A 2) P 3) A 4) P
Lesson 9: Advanced Punctuation
Semicolon (;)
Joins related independent clauses without a conjunction.
"The fear of Yahuah is the beginning of wisdom; fools despise wisdom."
Colon (:)
Introduces a list, explanation, or quotation after a complete sentence.
"Yahuah requires three things: justice, mercy, and humility."
Em Dash (—)
Creates dramatic pause or emphasis.
"Peter—the one who denied Him—became a bold preacher."
Choose: semicolon (;), colon (:), or em dash (—):
1. "Faith without works is dead ___ it must be demonstrated."
2. "The fruit includes these ___ love, joy, peace."
3. "Abraham ___ the father of faith ___ obeyed."
4. "Many are called ___ few are chosen."
Write a paragraph about the Exodus using at least one semicolon, one colon, and one em dash.
Answer Key - Lesson 9
Recall: 1) ; 2) : 3) — 4) ;
Lesson 10: Editing for Clarity
Good writers are good editors. The first draft is never the final draft.
"The words of the wise are like goads, and the words of scholars are like well-driven nails."
— Ecclesiastes 12:11Eliminate Wordiness
"Due to the fact that the Pharisees were in possession of pride..."
"Because the Pharisees were proud..."
Cut: "due to the fact that" → "because" | "in order to" → "to" | "at this point in time" → "now"
Use Specific Language
"David did a lot of good things."
"David defeated the Philistines, united Israel, and wrote psalms."
Problem: wordiness (W), vague (V), or grammar error (G)?
1. "Due to the fact that Paul had a thorn, he prayed."
2. "The disciples did stuff."
3. "Each of the apostles were given their mission."
Edit this paragraph:
"In order to follow Yahusha, the disciples had to gave up a lot of things. Due to the fact that he called them, they left they're nets. Peter who was called first became a important leader. Each of the twelve was given there mission."
Answer Key - Lesson 10
Recall: 1) W 2) V 3) G
Progress Tracker - Spaced Repetition
| Lesson | Day 1 | Day 3 | Day 7 | Day 21 | Day 60 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Sentence Structure | |||||
| 2. Phrases and Clauses | |||||
| 3. Verbals | |||||
| 4. Subject-Verb Agreement | |||||
| 5. Pronoun Case | |||||
| 6. Parallel Structure | |||||
| 7. Modifiers | |||||
| 8. Active vs. Passive | |||||
| 9. Advanced Punctuation | |||||
| 10. Editing for Clarity |