
Parts of speech
Types of sentences
Complex Sentences & Sentence Diagramming

Parts of speech

Types of sentences
Before we learn complex sentences, let's review the basics. A simple sentence has ONE independent clause - it contains a subject and a predicate (verb) and expresses a complete thought.
Example: "The wise man | built his house upon the rock."
Complete Subject: The wise man (simple subject: man)
Complete Predicate: built his house upon the rock (simple predicate: built)
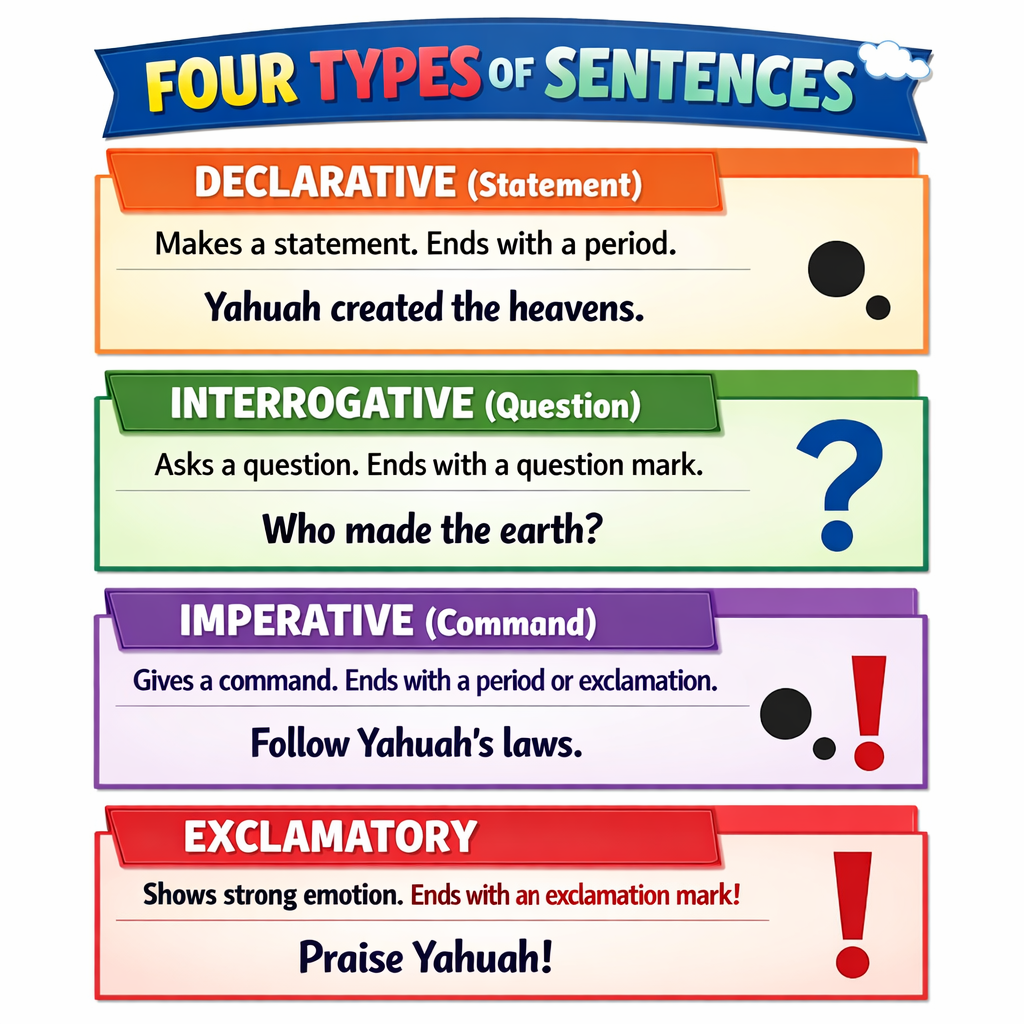
Four Types of Simple Sentences:
| Type | Purpose | End Punctuation | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Declarative | Makes a statement | Period (.) | Yahuah is good. |
| Interrogative | Asks a question | Question mark (?) | Is Yahuah good? |
| Imperative | Gives a command | Period (.) or (!) | Trust in Yahuah. |
| Exclamatory | Shows strong emotion | Exclamation mark (!) | How great is Yahuah! |
Notice how Scripture often uses simple, powerful sentences. "Elohim created" - just two words convey the most important truth! Good writing doesn't require complicated sentences; it requires CLEAR sentences that communicate truth.
1. Identify the simple subject and simple predicate:
a) The righteous man walks in integrity.
Simple subject: Simple predicate:
b) His children are blessed after him.
Simple subject: Simple predicate:
c) The heavens declare the glory of Elohim.
Simple subject: Simple predicate:
2. Identify the sentence type (declarative, interrogative, imperative, exclamatory):
a) Keep the Sabbath holy.
b) How wonderful are Your works!
c) Did Noah build the ark?
d) Yahusha is the Messiah.
Write the four sentence types and an example of each from Scripture or your own words:
Read aloud Genesis 1:1-5, identifying the simple subject and predicate in each sentence.
Quick Quiz:
1. A simple sentence has how many independent clauses?
2. The subject tells us __________ or __________ the sentence is about.
3. The predicate contains the __________.
Write three simple sentences about creation, one declarative, one exclamatory, and one imperative:
A compound sentence contains TWO or more independent clauses joined together. Each clause could stand alone as a simple sentence.
Common Conjunctive Adverbs: however, therefore, moreover, furthermore, consequently, nevertheless, meanwhile, otherwise
Simple sentences:
Moses led the people. They crossed the Red Sea.
Combined as compound:
Moses led the people, and they crossed the Red Sea.
Moses led the people; they crossed the Red Sea.
Moses led the people; consequently, they crossed the Red Sea.
Scripture uses compound sentences to show CONNECTED truths. In Psalm 19:1, both clauses tell us about creation's testimony - the heavens AND the firmament both declare Yahuah's glory. Compound sentences help us see how truths relate to each other.
1. Identify whether each sentence is SIMPLE or COMPOUND:
a) Noah built the ark, and Yahuah shut the door.
b) Abraham obeyed Yahuah and left his homeland.
c) Daniel prayed; the lions did not harm him.
d) David was a shepherd.
2. Combine these simple sentences into compound sentences using different methods:
a) Yahusha healed the sick. He taught the people.
With comma + conjunction:
With semicolon:
3. Choose the correct FANBOYS conjunction:
a) We should keep the Sabbath, __________ it is Yahuah's command. (for/yet)
b) The Pharisees questioned Yahusha, __________ He answered wisely. (but/or)
c) Repent of sin, __________ face judgment. (and/or)
Write the FANBOYS acronym and what each letter stands for:
Read Psalm 19:1-6 aloud. Identify compound sentences and what conjunction or punctuation joins them.
Write three compound sentences about the Exodus story (Moses, Egypt, Red Sea, etc.):
A complex sentence contains ONE independent clause and ONE or more dependent (subordinate) clauses. The dependent clause cannot stand alone - it depends on the main clause.
These words begin dependent clauses and show the relationship to the main clause:
| Time | Cause/Effect | Contrast | Condition |
|---|---|---|---|
| when, while, after, before, until, since, as | because, since, so that | although, though, whereas, while | if, unless, provided that |
Independent clause: Yahuah delivered Israel.
Dependent clause: Because they cried out to Him
Complex sentence: Because they cried out to Him, Yahuah delivered Israel.
OR: Yahuah delivered Israel because they cried out to Him.
Punctuation Rule:
Complex sentences show cause-and-effect relationships that are crucial in Scripture. "IF you love me, keep my commandments" (John 14:15). The condition (if) creates the dependent clause - our love for Yahusha is connected to our obedience!
1. Underline the dependent clause. Circle the subordinating conjunction:
a) Although the world rejected Him, Yahusha offered salvation.
b) Israel wandered in the wilderness until they reached the Promised Land.
c) When Daniel was thrown into the lions' den, Yahuah protected him.
d) The disciples rejoiced because Yahusha had risen.
2. Identify whether each sentence is SIMPLE, COMPOUND, or COMPLEX:
a) After the flood receded, Noah built an altar.
b) David sinned, but he repented.
c) Yahuah is faithful.
d) If you confess your sins, He is faithful to forgive.
3. Add the correct punctuation (comma or nothing):
a) When Yahusha returns__ the dead in Messiah will rise first.
b) The Israelites celebrated__ after they crossed the Red Sea.
c) Because Yahuah is merciful__ we have hope.
List five subordinating conjunctions and write an example sentence for one:
Rewrite these simple sentences as complex sentences by adding a dependent clause:
a) Yahuah blessed Abraham. →
b) The disciples were afraid. →
c) We should pray. →
A compound-complex sentence contains at least TWO independent clauses AND at least ONE dependent clause. It's the most sophisticated sentence structure!
Compound-Complex = 2+ Independent Clauses + 1+ Dependent Clause
Analysis:
"When Yahusha called, Peter left his nets, and he followed the Master."
| Sentence Type | Independent Clauses | Dependent Clauses |
|---|---|---|
| Simple | 1 | 0 |
| Compound | 2+ | 0 |
| Complex | 1 | 1+ |
| Compound-Complex | 2+ | 1+ |
1. Identify the sentence type (simple, compound, complex, compound-complex):
a) Although Moses was afraid, he obeyed Yahuah, and he confronted Pharaoh.
b) Yahuah is righteous, and His judgments are true.
c) When the trumpet sounds, the dead will rise, and we will be changed.
d) David was a man after Yahuah's own heart.
2. Break down this compound-complex sentence:
"Because the disciples believed, they left everything, and they followed Yahusha."
Dependent clause:
Independent clause 1:
Independent clause 2:
Write one compound-complex sentence about the story of Noah and the Flood:
Sentence diagramming is a visual way to show how words in a sentence relate to each other. It helps us understand grammar deeply!
The main line shows the subject and predicate (verb), separated by a vertical line:
Sentence: "Yahuah created."
Adding a Direct Object:
A direct object receives the action of the verb. It goes after the verb, separated by a line that stops at the main line:
Sentence: "Elohim created the heavens."
(Note: In actual diagramming, the direct object line doesn't pass through the main line)
Diagramming helps us see sentence structure clearly - just as studying Scripture helps us see TRUTH clearly. When we break down a verse into its parts, we understand it better. "In the beginning / Elohim / created / the heavens and the earth" - each part has a role!
Diagram these simple sentences (Subject | Verb | Direct Object):
a) Moses led Israel.
b) David killed Goliath.
c) Yahusha healed the sick.
Diagram Genesis 1:1: "In the beginning Elohim created the heavens and the earth."
(Hint: "the heavens and the earth" is a compound direct object)
Modifiers (adjectives and adverbs) go on diagonal lines UNDER the word they modify.
Sentence: "The faithful servant worked diligently."
Structure:
The diagonal lines under "servant" show: The / faithful
The diagonal line under "worked" shows: diligently
1. Identify the modifiers and what they modify:
a) The righteous man prays earnestly.
Adjective(s): modifies:
Adverb(s): modifies:
b) Yahuah's great love never fails.
Adjective(s): modifies:
Adverb(s): modifies:
2. Diagram with modifiers:
a) The good shepherd protects carefully.
b) Wise men sought the young child diligently.
When a sentence has compound subjects, compound verbs, or compound objects, we show them on forked lines.
Compound parts are joined by a conjunction (and, or, but). In diagrams:
Compound Subject: "Moses and Aaron led Israel."
Both "Moses" and "Aaron" are subjects, connected by "and"
Compound Verb: "David sang and danced."
Both "sang" and "danced" are verbs, connected by "and"
Compound Object: "Yahuah created the heavens and the earth."
Both "heavens" and "earth" are direct objects, connected by "and"
1. Identify the compound parts:
a) Peter and John went to the temple.
Compound: Type:
b) Mary pondered and treasured these things.
Compound: Type:
c) The disciples caught fish and bread.
Compound: Type:
2. Diagram:
Abraham and Sarah believed Yahuah.
In complex sentences, the dependent clause goes on a separate line BELOW the main clause, connected by a dotted line from the subordinating conjunction.
Sentence: "When Yahusha called, Peter followed."
Main clause: Peter followed
Dependent clause: When Yahusha called
The dependent clause modifies the verb "followed" (tells WHEN)
Diagram these complex sentences:
a) Because Yahuah loved the world, He sent His Son.
b) The disciples rejoiced when Yahusha appeared.
Let's go deeper into understanding clauses - the building blocks of sentences.
| Type | Function | Introduced By | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverb Clause | Modifies verb (tells when, where, why, how) | Subordinating conjunctions | When Moses stretched his hand, the sea parted. |
| Adjective Clause | Modifies noun | Relative pronouns (who, whom, whose, which, that) | The man who trusts in Yahuah is blessed. |
| Noun Clause | Acts as noun (subject, object, etc.) | that, what, whoever, whatever, etc. | What Yahuah has promised will come to pass. |
1. Identify the type of dependent clause (adverb, adjective, or noun):
a) The disciples believed what Yahusha taught.
b) Israel wandered because they disobeyed.
c) The temple that Solomon built was magnificent.
d) Whoever believes in Him will not perish.
2. Underline the dependent clause and identify its type:
a) Abraham, who believed Yahuah, was counted righteous.
Type: Function: modifies
A phrase is a group of related words that does NOT have both a subject and a verb. Phrases add detail to sentences.
Common Prepositions: in, on, at, by, for, with, from, to, through, during, before, after, above, below, under, between, among, around, behind, beside, into, onto, upon, within, without
1. Identify the prepositional phrases (there may be more than one):
a) Moses went up to the mountain of Yahuah.
Prepositional phrase(s):
b) The Israelites walked through the Red Sea on dry ground.
Prepositional phrase(s):
c) David hid in the cave from Saul.
Prepositional phrase(s):
2. Add prepositional phrases to expand these sentences:
a) Yahuah dwells. → Yahuah dwells
b) The disciples traveled. → The disciples traveled
Subjects and verbs must agree in number. Singular subjects take singular verbs; plural subjects take plural verbs.
Choose the correct verb:
a) The law of Yahuah (is/are) perfect.
b) David and Jonathan (was/were) friends.
c) Neither sin nor death (has/have) power over believers.
d) The congregation (worships/worship) together.
e) The books of Moses (tells/tell) the history of Israel.
Now let's apply everything we've learned to analyze Scripture!
1. Analyze John 3:16:
a) What type of sentence is this?
b) How many independent clauses?
c) How many dependent clauses?
d) Identify a prepositional phrase:
2. Identify sentence types:
a) "In the beginning was the Word, and the Word was with Elohim, and the Word was Elohim."
b) "If you love Me, keep My commandments."
c) "Yahuah is my shepherd."
3. Diagram Psalm 23:1:
"Yahuah is my shepherd."
Write a paragraph (4-5 sentences) about your favorite Bible story. Include:
Now label each sentence type and underline your prepositional phrases!
Lesson 1:
1a) man / walks; 1b) children / are; 1c) heavens / declare
2a) imperative; 2b) exclamatory; 2c) interrogative; 2d) declarative
Lesson 2:
1a) compound; 1b) simple (compound verb, single subject); 1c) compound; 1d) simple
Lesson 3:
1a) Although the world rejected Him / Although; 1b) until they reached the Promised Land / until
2a) complex; 2b) compound; 2c) simple; 2d) complex
Lesson 4:
1a) compound-complex; 1b) compound; 1c) compound-complex; 1d) simple
2) Dependent: Because the disciples believed; Ind 1: they left everything; Ind 2: they followed Yahusha
Lesson 9:
1a) noun; 1b) adverb; 1c) adjective; 1d) noun
Lesson 10:
1a) to the mountain, of Yahuah; 1b) through the Red Sea, on dry ground; 1c) in the cave, from Saul
Lesson 11:
a) is; b) were; c) has; d) worships; e) tell
Lesson 12:
John 3:16: Complex (or compound-complex depending on analysis); "in Him" is prepositional phrase